Lithium batteries
2023/07/06 11:11:35
Lithium batteries are a class of batteries made from lithium metal or lithium alloys as positive/negative electrode materials, using a non-aqueous electrolyte solution. lithium metal batteries were first proposed and studied by Gilbert N. Lewis in 1912, and in the 1970s, M. S. Whittingham proposed and began to study lithium ion batteries. The chemical properties of lithium metal are very active, which makes the processing, preservation and use of lithium metal, very demanding on the environment. With the development of science and technology, lithium batteries have become mainstream.
Lithium batteries can be broadly divided into two categories: lithium metal batteries and lithium ion batteries. Lithium-ion batteries do not contain lithium in its metallic form and are rechargeable. The fifth generation of rechargeable batteries, the lithium metal battery, was created in 1996 and has better safety, specific capacity, self-discharge rate and performance to price ratio than lithium ion batteries. Due to its own high technical requirements, only a few companies in a few countries are producing these lithium metal batteries.
Principle of operation
Lithium metal batteries:
The basic principle of lithium batteries
Lithium metal batteries are generally batteries that use manganese dioxide as the cathode material and lithium metal or its alloy metal as the negative material, using a non-aqueous electrolyte solution.
Discharge reaction: Li + MnO2 = LiMnO2
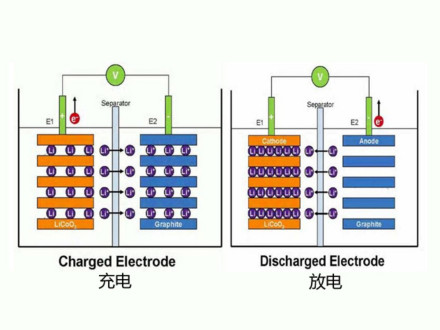
Lithium ion batteries:
Lithium ion batteries are generally batteries that use lithium alloy metal oxide as the positive electrode material, graphite as the negative electrode material and a non-aqueous electrolyte solution.
The reaction that occurs at the charging cathode is
LiCoO2 = Li(1-x)CoO2 + xLi + + xe- (electrons)
The reaction occurring on the negative side of the charge is
6C+xLi++xe- = LixC6
Total reaction in the charge cell: LiCoO2 + 6C = Li(1-x)CoO2 + LixC6